When creating and editing target groups, users can be assigned to a target group via rules as well as be defined as an exception. In addition to the description tab, which contains general information about the target group, the two other tabs "Rules" and "Exceptions" are also available. Target groups can, for example, be used for automatic course registration. All users assigned to a target group are automatically registered for a course.
Description
The tab will refresh with a new screen to commence building the Target Group. The first step is to populate the 'Description' tab and the main fields and settings are described below:
-
Status: Will need to be “Active” to use.
-
Function: Determine if the Target Group has specific functional capability; e.g. having users selected as Tutors or Course Administrators.
-
Comment of changes: For compliance purposes each time a Target Group is created or edited a comment must be entered in this field.
-
Automatic update of groups members: Needs to be checked to have the rules process each day to update the participant list.
-
Manager: The user that receives updates about updates to the participant list. There is no Supervisor-type reporting lines.
-
Clients / Groups: These are basically to restrict the pool of users from where the rules will consider. If blank all users in the system are considered in rules created in the “Rules” tab.
-
Name: Name for the Target Group which will be available in each active system language.
Rules
A complex set of rules and conditions can be stored on the "Rules" tab, from which the users who are assigned to the target group can later be derived. A rule is the framework in which the conditions are defined. Two different types of rules are distinguished between:
-
Inclusive rule: All users who meet the conditions of this rule are later included in the target group.
-
Exclusive rule: The users who meet the conditions of this rule are explicitly excluded from the target group.
Which of the two types of rules is used depends on the users who should be present in the target group. If a rule was created, different conditions can be added, which are connected with one another by a logical "AND." Multiple rules of a rule set are interconnected by a logical "OR." A diverse set of selection criteria is available for this: course groups, learning paths, course templates, courses, skills, job profiles, groups and personal identifiers.
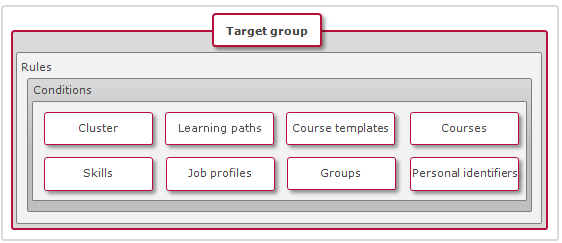
Different comparison operators can be used depending on the selection of the criterion.
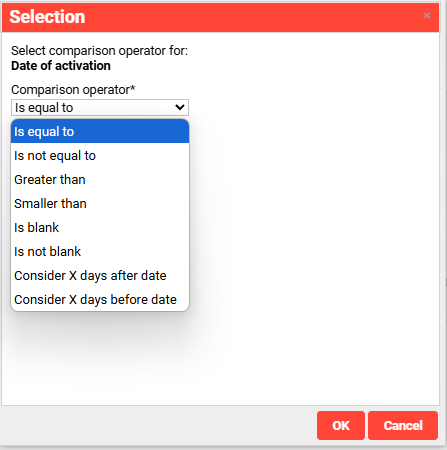
Thus, for example, the following scenarios illustrate:
A target group should consist of users who
-
have completed a course from a selected course group at least five months ago
-
have completed a selected learning path prior to 31 December 2011
-
have completed a course from a selected course template with version number 1.0 after 31 December 2011
-
have completed a selected course prior to 31 December 2011
-
have a selected skill with at least 80 points
-
have a selected job profile
-
belong to a selected system group, organisational unit or target group
-
correspond / do not correspond to a certain value of a personal identifier
-
correspond to a group that have completed the probation period after X days
-
have failed a certain course/ learning path (condition that the enrolment status of the course/learning path is “failed”)
Very complex target group formations can also be defined from this set-up. As a target group may contain exactly one different target group, nested structures may result.
Exceptions
In some cases, it is necessary that exceptions can be created for the defined rules. When adding exceptions, it can be decided whether it is an inclusive or an exclusive exception:
-
Inclusive exception: Users who are included are always in the target group, regardless of whether they meet the conditions on the "Rules" tab or not.
-
Exclusive exception: Users who are excluded are not included in the target group if they meet all of the conditions.
The inclusion or exclusion of users can take place manually by selecting users from a pop-up or can be carried out by import. In both cases, additional information can be defined, such as a reason or a comment on creating an exception.
When using rules and conditions together with exceptions, a special processing sequence is observed:
-
Exceptions stand above all other rules and conditions and are always given priority, whereby an exclusion is always more important than an inclusion
-
For rules and conditions, the exclusion is always more important than the inclusion of users
